<slider>
What do we mean with creativity? Talking about creativity is not easy. It corresponds to turning new and imaginative ideas real. It refers to the ability to recognise the world in new ways finding hidden patterns, turn real connections between initial non connected events and be able to raise innovative solutions.
In order to create we need to think and then execute. Having new ideas but staying still, means that someone is imaginative but not creative.
The sampled crafts here below believed in their ideas and decided to be creative.
Being creative is defined as a skill that can effectively be developed and a process able to be managed. It starts with a foundation of knowledge, by learning a discipline but certainly by mastering a way of thinking. Any person can learn how to be creative. You can experiment, explore, question assumptions, use ideas, imagination and taught and learn it by understanding how to synthesise information.

</slider>
<slider>
Creativity and Innovation Many questions and statements arise around creativity and innovation because the two are different concepts but interrelated.
“
Creativity is the capability or act of conceiving something original or unusual.”
“
Innovation is the implementation of something new.”
“
Invention is the creation of something that has never been made before and is recognized as the product of some unique insight.”
</slider>
<slider>
What are the sources of creativity?
There are many different viewpoints about the creativity definition. The challenge lies partially in the nature and definition of creativity. It may take many forms and it may be found in a variety of contexts.
It may be embodied by individuals with a broad range of personal characteristics and different backgrounds. It is not only the destiny of some but a possibility to all. We just need to believe in ourselves and do not wait to put in practice the new ideas that emerge.
While doing brainstorm meetings we can think about dozens of new ideas. We are thus evidencing creativity but it will only turn into innovation when it will be implemented. So, we need to take risks in order to a creative idea would be turned into an innovation.
A product, a service, a device or a method that did not existed previously are considered inventions and every invention is seen as innovation. But the other way around is not always true.

</slider>
<slider>
What are the sources of creativity?Creative thinking: relates to how flexibly and imaginatively people approach problems. It depends on personality and thinking or working style
Personality: thinking or working style
Knowledge: all the relevant understanding an individual brings to bear on a creative effort, demanding expertise which can be on the form of technical knowledge, procedural or intellectual
Motivation: generally accepted as key to creative production, and the most important motivators are intrinsic passion and interest in the work itself
</slider>
<slider>
What are the sources of creativity? Creative skills are not just about good ideas, are also about having the skills to make good ideas happen, such as imagination, self-motivation, resilience, collaboration, responsibility.
We may find several explanations for creativity. It may be seen as a property or characteristic of human beings, converted into a very important change in the organizational world.
Creativity is not only being original; it is something beyond positive psychological characteristics. That is why a reasonable definition may not be provided and there is no consensus in this subject.
</slider>
<slider>
What are the sources of creativity?
To understand what creativity means we need to analyze:
- Context
- Creativity product
- Creation process
- Cognitive characteristics of the creative person
</slider>
<slider>
1. Context We need to observe all the elements which constitute a situation in which creative processes emerge. The combination of elements composing the context may have a catalytic or inhibitory effect.
Case studies:The new lens developed by REG’ART (
Case 1) were a unique model that the director wanted to show in his business. It took time to develop the innovation, and it was a time of some major difficulties. The finished product was not intended for sale, but the buyer was found immediately at the end provided the process was so original.
What makes MF Ceramics (
Case 7) a success and an innovative case is Margarida autonomy and independence in the creative process and at same time the deep connection with her influences and roots.
When Sónia still had the children´s decoration store open (Rosabengala,
Case 10), Sónia decided to try do something different in collaboration with another designer. They organized an exhibition with their work and it was a success.

</slider>
<slider>
1. Context (cont.)Rui Viana (Piurra,
Case 8) was born in a family of wood craftsman. During his studies and already employed, Rui never stopped dreaming and planning a more independent path in the furniture market. With a very particular vision in mind, he challenged the owner of this company and his boss to create a new furniture brand.

Beleza do Sal (
Case 9) wants to differentiate from the competition not only by unique and quality products (without chemicals), but also by using eco-friendly and recyclable packaging, promoting regional products (e.g. through the incorporation of salt and algae in its products) and adopting handmade processes.

</slider>
<slider>
2. Creativity productThe final result is a combination of behaviors, incomes, ideas, objects and any other kind of human activity.
Creativity as creative income cannot be measured with great objectiveness and so depends over a set of criteria’s hardly applied in the traditional psychological evaluation.
Kurelu (
Case 4) has introduced several innovations in the weaving:
- New materials and textiles
- Modern patterns
- A loom patent

Centro Cerámica Talavera (
Case 11) is the example about how to face the economic crisis by using creativity and without losing quality and the sight of the traditional ceramics. “
We wanted to renew ourselves within the tradition, continue the process of evolution, always with the utmost respect”.
</slider>
<slider>
3. Creation processIncludes all mental operations which composes the “creative taught”. It is also related to cognitive characteristics of a creative person.
Some persons assume that all the creativity activity emerges from previous existent experiences in the brain, as a result of internal and external perceptions.
Creativity may be understood as an interaction of cognitive processes, a characteristic of personality, thinking styles and environmental conditions, which occur on the basis of the family, professional or social context.
Being art school trained and following her own learning path, immersing herself in the process with different professional cultures and learning distinct techniques, provided Margarida (MF Ceramics,
Case 7) the basis for the development of a certain way of making ceramic products. This, allied to an outstanding visual culture, created her signature style.

</slider>
<slider>
4. Cognitive characteristics of the creative person (cont.). How does creative thinking emerge?
Creativity cannot be seen as something only available for artists and inventors. In reality, human mind has a creative impulse integrated in its operative system, integrated in its most basic programming code. As such, any one may give rise to creative ideas!
The individual, as a creative human being, has some psychological characteristics which turn him a creative person in both relative and absolute terms. So, we may include intellectual factors, personality, motivation and variability in the use of creative thinking.
So, the creative thought emerges from the combination of cognitive capacities of individuals with factors like temperament and character. It may happen from several perspectives.
It may be a process of becoming aware of the difficulties, problems, missing information, missing elements, anomalies, to make mistakes and formulate hypotheses about deficiencies, to evaluate errors and hypotheses, possibly review them and prove them, and in the end, communicate their results.

</slider>
<slider>
4. Cognitive characteristics of the creative person (cont.). How does creative thinking emerge?
In the middle of economic crisis in Greece, Irini Papadopoulou (One & Only,
Case 3) quit her career on marketing and sales and returned to an old passion she had left behind many years before: traditional crochet and knitting. Inspired by a famous Italian brand and driven by her passion, talent and high aesthetic, she started ideating and creating in home her own crochet bags by combining the greek heritage of crochet with the latest fashion trends.

Florentin Robert (REG’ART,
Case 1) obtained his BTS Optician’s diploma and before specializing in contactology, optometry and low vision, taking a bachelor’s degree. The challenge that the young manager faced was how to publicize and develop his business? Creating custom glasses, that were adapted to the customer’s anatomy and tastes. To do this, he used unusual materials to make unique designs. The latest innovation is a fully inlaid lens, which he has created by developing a process involving a stream of water.

</slider>
<slider>
4. Cognitive characteristics of the creative person (cont.). How does creative thinking emerge?
As such, creativity is a person’s capacity to produce ideas, discoveries, restructuring, inventions, and new and original artistic objects, which are accepted by specialists as valuable elements in the science, technology and art domains.
Originality, utility and value are properties of the creative process. Creativity also demands that opportunities are taken out as in the cases pointed previously.
Sometimes opportunities emerge and we need to know how to take advantage from these, especially in the crafts area. </slider>
<slider>
4. Cognitive characteristics of the creative person (cont.). How does creative thinking emerge?“
Thinking draws upon logic, imagination, intuition and systematic reasoning, to explore possibilities of what could be and to create desired outcomes.”
</slider>
<slider>
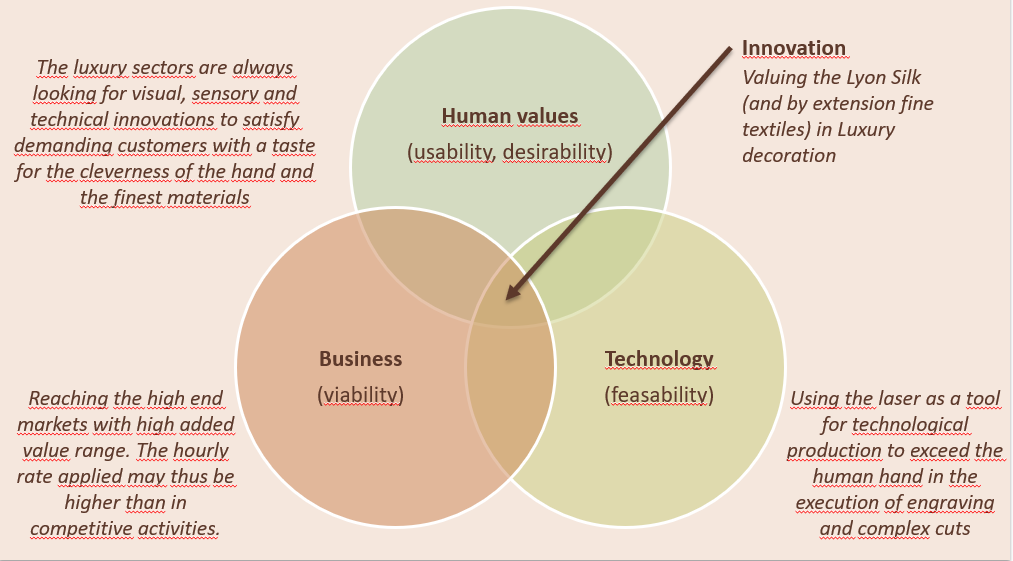
4. Cognitive characteristics of the creative person (cont.). How does creative thinking emerge?The founder of YUME PEMA (
Case 2) works according to Design Thinking approach. Here is how the 3 pillars of this method are used to develop the innovative marquetry process:
</slider>
<slider>
Some ways to develop your creativity Examine and remove perceptual blocksAvoid quick decisions and conclusions, look for alternatives.
Recognize and overcome limited resources Think how you can make your idea work, who are available who might help you and how you can substitute the expensive resources you think you need.
Practice divergent/convergent thinking Generate multiple answers to a problem or put diverse and disparate ideas, concepts and objects together to create a new object, idea or concept.
Collaborate Share your thoughts promote the divergent/convergent thinking and then the production of more alternatives and diverse ideas.
Learn Creativity requires knowledge. Generally, the most creative people are those who can apply the knowledge from one domain to another.
</slider>
<slider>
Among the cases, we can find examples of craftsmen for whom collaboration and learning were key for the creative process.
After years of survival at the Workshop, the artisans of Centro Cerâmica Talavera (
Case 11) organized the "Work in progress" exhibition to celebrate the Center's 15th anniversary. The commissioner proposed to invite new artists from different areas (e.g. textiles, plastic art, graphite, etc.) to use ceramics as a medium. Among those who accepted the invitation were the trio of Rubenimichi painters. Ceramic skulls were created by them within this collaboration.

Margarida Fernandes, the founder of MFCeramics (
Case 7) decided to embrace the ceramic craft after some stents at design studios. However, after making some unsuccessful contact with Portuguese workshops, she went to Denmark where she learned new techniques. Being a woman, young and educated, she was probably far from the “normal type” in her homeland traditional male oriented pottery “industry”. After Denmark, Margarida went to Amsterdam where she had the opportunity to learn different techniques. After this Northern European experience, Margarida returned to Portugal and opened her own studio in the family’s garage at Lisbon outskirts.
</slider>
<slider>
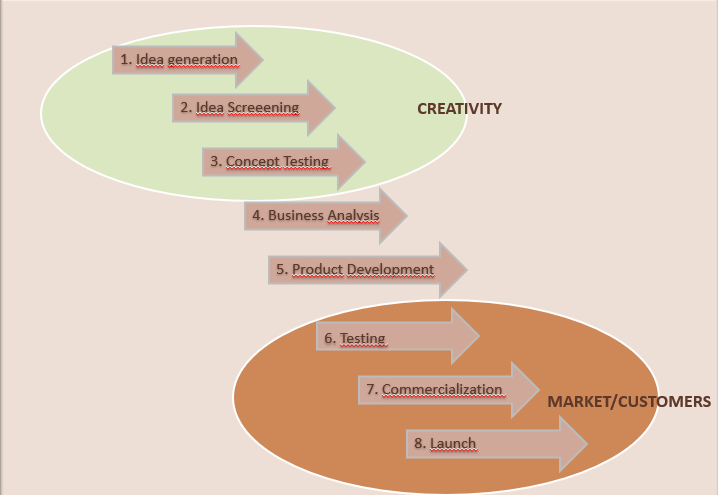
New Product Development Cycle (in Crafts)
</slider>
<slider>
New Product Development Cycle (in Crafts)
Is the development of a new product idea hard to implement? Unfeasible?
The answer is clearly no… There is an easier way… you just have to follow a structural roadmap…
1. Idea generation
In Crafts we start from developing a product with a concept.
To a certain extent, the rest of the process guarantees that new and creative ideas are tested for viability. At least, at the beginning all ideas are good ideas, or creative person think always they are!
WHERE TO GET IDEAS? We could start with a SWOT analysis (strenhts, weaknesses, opportunities and threats).
With the SWOT you could be able to analyse the craft position and find a direction in line with business strategy.
Ensure that:You incorporate current market trends in the
SWOTYou previously
study the marketYou undertake effective
market research You listen to
target audience suggestionsYou
encourage suggestions from employees and partners
You look at other craft competitor´s
successes and
failures </slider>
<slider>
New Product Development Cycle (in Crafts)2. Idea screening
This step is extremely necessary to ensure that unsuitable ideas would be rejected right away. At this stage you need to look at return on investment, affordability, market potential, and look at this carefully to avoid future market failure after initial investment realized.
You could also be creative here by adapting least expensive materials and thinking about innovative new materials and production process able to allow you to reduce costs.

</slider>
<slider>
New Product Development Cycle (in Crafts)3. Concept testing
The idea you have needs to be tested with customers to observe their reaction.
The idea should now be a concept with enough detailed information such that your future customers can visualize it.
Be sure that:They understand the concept
They need it or want it
Considering their feedback,
adapt the concept, start the thinking about the marketing message and simply BE EVEN MORE CREATIVE.

</slider>
<slider>
New Product Development Cycle (in Crafts)4. Business analysis
You will need a business case once the concept is tested and finalized.
WHY IS THAT SO?You also need to access whether the new crafts product or service will be profitable.
As such, you need a detailed marketing strategy including:The target market
Product positioning
Marketing mix to be used
 And answer or include the following in this analysis:
And answer or include the following in this analysis:Demand for the product exists?
Full appraised of the costs exists?
Competition exists?
Identification of a break-even point?
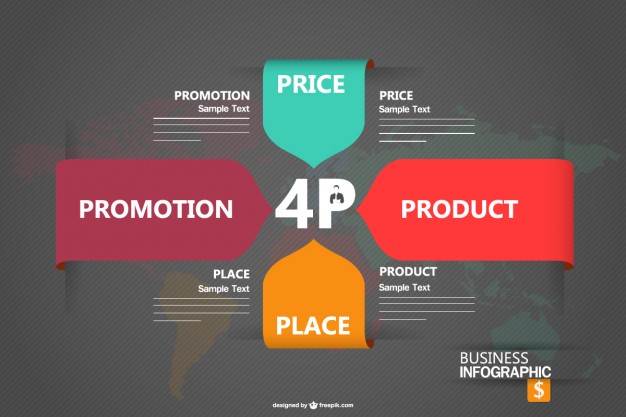
Marketing strategy/business analysis is comprised of four Ps:
Product, Price, Promotion and Placement
</slider>
<slider>
New Product Development Cycle (in Crafts)5. Product Development
After being approved we start the technical and marketing development phases, meaning, the creation of the prototype.
In the crafts case, usually we do not have massive production and each product turns out to be distinct from the rest because each as a little difference in creative terms.
In this phase design and specification research is pursued and manufacturing methods are explored.
6. Testing
This phase introduces the prototype product following the market plan.
It is required to ensure that the whole concept is correct and to refine elements from product to marketing.
</slider>
<slider>
New Product Development Cycle (in Crafts)
7. Commercialisation Phase of final decisions to take the product to its launching in the market.
The steps where price and marketing plans are finalized. Moreover, teams sales, distribution channels or exposition ways are designed in order to guarantee the product is ready for the final stage.
8. Launch A launch plan is needed now…
This ensures a smooth and maximum impact into the market.
For this to go well a review of market performance is mandatory for the project success.
 WHAT SHOULD WE LEARN?
WHAT SHOULD WE LEARN?
Although product development is creative, there exists the need for discipline and the need to follow basic steps in this process.
</slider>
<slider>
New Product Development Cycle (in Crafts)Identification of design criteria: involves brainstorming
Idea analysis: closer evaluation of product concept (market research and concept studies)
Concept genesis: turning identified product opportunities into tangible concepts
Prototyping: “quick-and-dirty” model
Product development: “give life” to an idea (the crafts product has business sense and value)
WHAT ABOUT DESIGN THINKING? Design thinking has interactive steps that are drawn to be followed in a particular order to promote creativity and collaboration:
Empathize: learn more about the problem from multiple perspectives
Define: identification of the scope and problem true nature
Ideate: Brainstorming problem solutions (a new product can be an existent one but with another perspective)
Prototype: weed out unworkable or impractical solutions
Test: ask for feedback
</slider>
<slider>
Applying the concepts to your context

1. Think about other businesses in crafts and semi-industrial activities sectors that you know, based in your community, country or even in other countries. How did the context influence the creative process?
What were their sources of creativity?
2. Now think about your business. How would you describe your business according to the three pillars of Design Thinking?
What strategies could you adopt to develop your creativity?
</slider>